Dummy
ACL cause symptoms and treatment
Information on the anterior cruciate ligament injury.
When faced with a torn anterior cruciate ligament, you will undoubtedly be left with questions. Probably the most important question is whether a anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction noodzakelijk is, of dat herstellen zonder operatie ook mogelijk is (conservatief). Om deze vragen te beantwoorden, is het essentieel om eerst te begrijpen wat de voorste kruisband precies is en verkennen we de oorzaken, symptomen en behandeling. Hier lees je alles over de voorste kruisband blessure.
General
Cause
Symptoms
Exam
Treatment
What is an anterior cruciate ligament?
In the middle of the knee are the anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments. They cross each other and are therefore called cruciate ligaments. The anterior cruciate ligament can support about five to six times the body weight. The anterior cruciate ligament consists of two bundles four centimeters long and together are one pinky finger thick.
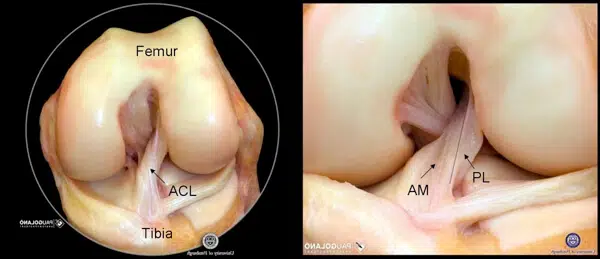
One bundle prevents the tibia from sliding forward relative to the femur. The other bundle prevents rotation of the tibia. In addition to being a stabilizer, the cruciate ligament is also a sensor. Through complex reflexes, muscles are controlled in milliseconds. The function of the knee depends on a good muscular system that, together with the other ligaments and fascia, provides stability. With a torn or insufficient anterior cruciate ligament, the anterior and posterior instability can be handled well with training. Rotational instability is much more difficult to resolve with training and usually results in an unstable knee with sports.
What is the cause of an anterior cruciate ligament injury?
The anterior cruciate ligament tears in 45 milliseconds. A trained athlete can tighten his muscles in 80 milliseconds. So in some situations, simply put, you're just too late. In sports, changing direction, landing after a jump or slowing down after a sprint are the most common causes of a cruciate ligament tear. This always involves a deceleration of speed.
The chance of tearing the anterior cruciate ligament during a match is 10 percent higher compared to training. During a match, it's all about something. You don't want to lose and will put in just that extra step or acceleration to grab the ball, for example. This can put the body in positions where the muscle system cannot adequately control the knee. It almost always involves non-contact trauma. "There was no opponent around" is what clients often say.
Women are about 25 percent more likely than men to tear their cruciate ligament. The same percentages apply in young people under the age of 21. In addition, young people are more likely to have a re-rupture (tear again) after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Before returning to the sports field, proper rehabilitation, patience and taking your time are essential.
Risk factors
- Female gender young athlete (<21)
- Turn sports ( pivoting high impact sports) such as field hockey, soccer, basketball, handball, skiing etc.
- Hypermobiliteit
- Hormonal
- Weak hamstrings
- Reduced trunk stability

Contact trauma
A contact trauma is a knee injury caused by the acting force from outside. A shoulder thrust or collision between two athletes are examples of contact trauma. An accident in traffic or a fall down the stairs are high-energy traumas. Contact trauma and accidents are generally more serious injuries than noncontact trauma.
During skiing, percentage-wise, compared to other sports, most cruciate ligament injuries occur. Not counting the apres ski. Team sports such as basketball, handball, field hockey and soccer are also notorious for cruciate ligament injuries.
What are the symptoms and complaints of a torn anterior cruciate ligament?
First, there has been a trauma moment. Usually the foot is fixed on the ground and you twist the knee by braking abruptly, changing direction or landing after a jump. At the moment of injury, you may hear a tearing sound or pop. As a rule, overstretching or twisting the knee also strains or tears (partially) the knee capsule. The inner or outer ligament and/or meniscus may tear (partially). After the rupture of the cruciate ligament, slight to severe swelling occurs in the knee. This is because small blood vessels in the cruciate ligament rupture and start bleeding.

Swelling limits bending and stretching. The knee feels stiff and movement is difficult. Sometimes you feel nauseous or dizzy immediately after the trauma when you want to stand and walk. You may have muscle pain in your hamstrings in the following days. The knee is painful for the first few weeks and is usually in a slight flexion because of the swelling.
It is important to keep the knee exercises do. Therefore, do not put a pillow or any other object in the hollow of the knee. The knee will stiffen and intensive exercise is required to regain full extension. A locked knee due to a rotated meniscus is a reason that full extension is not possible. meniscus injury

Upper leg strength will decrease rapidly and significantly due to fluid in the knee (reflex inhibition). Less muscle strength means decreased stability, coordination and reflex movement. The chance of slipping through the knee again in the first few months with an unexpected movement increases. The knee is affected. "The heart attack of the knee" is what orthopedic surgeon van der Hart calls it. The patient experiences the sensation of the lower leg sinking away relative to the upper leg (sensation of knuckles rubbing together). This is called "giving away.
After tearing the cruciate ligament, the pain subsides quickly. The capsule of the knee and the inner or outer ligament may remain sensitive for a long time. Many people experience long-term bone bruising (bone bruise). This can last an average of three to six months. It eventually recovers on its own.
A torn cruciate ligament can cause instability while walking and during unexpected movements. After targeted rehabilitation, restrictions in daily life decrease and even running is often possible again. Sports involving contact and turning and twisting are generally not recommended. It is important to assess this in close consultation with your doctor and physical therapist.
How do you examine a torn anterior cruciate ligament?
Diagnosis is fairly easy by asking pointed questions and performing physical examination. The prerequisite is that the examination is done by an experienced knee specialist. In fact, in practice, an anterior cruciate ligament tear is frequently missed. A cruciate ligament tear hurts at the moment of rupture. This pain usually subsides quickly afterwards. Other structures damaged during the injury (meniscus, capsule, etc) usually remain painful for longer. Based on the pain location, a misdiagnosis can easily be made.
The knee is best examined immediately after the knee injury. With increasing swelling, pain and high muscle tension, the reliability of the examination decreases rapidly. After an average of seven to 10 days, the reliability of the examination increases again.
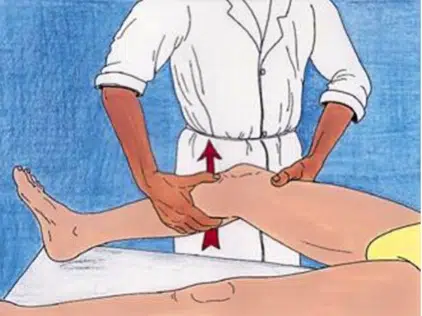
If an anterior cruciate ligament injury is suspected, the family doctor or physical therapist will refer you to an orthopedist. The orthopedist again asks a number of questions and assesses the knee. Based on his findings, the doctor will suggest an MRI. The MRI can be used to subtly assess the structures in the knee. Based on the MRI, a definitive diagnosis can be obtained and a treatment plan drawn up.
What does treatment for a torn anterior cruciate ligament look like?
After diagnosing the anterior cruciate ligament injury, there are two options. Conservative rehabilitation or surgery to reconstruct the anterior cruciate ligament.
The impact of the injury is significant. The limitations experienced in daily life and sports are reasons for many people to want surgery. It is, as mentioned, not black and white. Plenty of research has been done on the positive effects of conservative treatment. Sports are usually possible without a cruciate ligament. However, the type of sport and level must usually be adjusted. A cruciate ligament reconstruction is a choice and only necessary if you want to play high-intensity sports or experience instability in daily life (giving away).
An elite athlete or professional usually always undergoes surgery. In all other cases, the doctor will meet with you and discuss the pros and cons of surgery. In addition, each individual's situation must be assessed to determine the best treatment.

A knee after an anterior cruciate ligament injury generally recovers well. The fluid drains away, flexion and extension recover, and strength returns with targeted exercise. How long it takes and whether the knee fully recovers depends on any other injuries. The cruciate ligament does not grow, but sometimes attaches to the posterior cruciate ligament. This restores some stability to the knee.
Knee rehabilitation is a two-part process. On the one hand, you work with your physical therapist on recovery and, on the other hand, you go through the diagnostic process with the orthopedist. One pathway does not affect the other. Making a diagnosis takes time: that goes for making an appointment with the orthopedist through your family doctor, but also for waiting for an MRI and the results.
Various sports are possible without a cruciate ligament. Mainly straightforward sports such as rowing, cycling, running and even running a marathon could be possible. Continuing the conservative course is then a viable option. If you do have instability issues in sports, then you have the choice of considering another sport or surgery. Instability in daily life is usually always an indication to operate.
Want to know more about treatment? click here
Links:
